
Those resources include memory, RAM, storage, etc.

Then, it can divide itself into several independent “virtual machines.”Įach of these new virtual machines can then run their own operating systems and applications independently while still sharing the original resources from the bare metal server, which the hypervisor manages. When a hypervisor is used on a physical computer or server, (also known as bare metal server), it allows the physical computer to separate its operating system and applications from its hardware. While this technology can go by many names, including virtual server, virtual server instance (VSI) and virtual private server (VPS), this article will simply refer to them as virtual machines. It keeps each VM separate from others so they don’t interfere with each other. The hypervisor allocates physical computing resources-such as processors, memory, and storage-to each VM. Instead, it needs a lightweight software layer called a hypervisor to coordinate between it and the underlying physical hardware. A VM cannot interact directly with a physical computer.
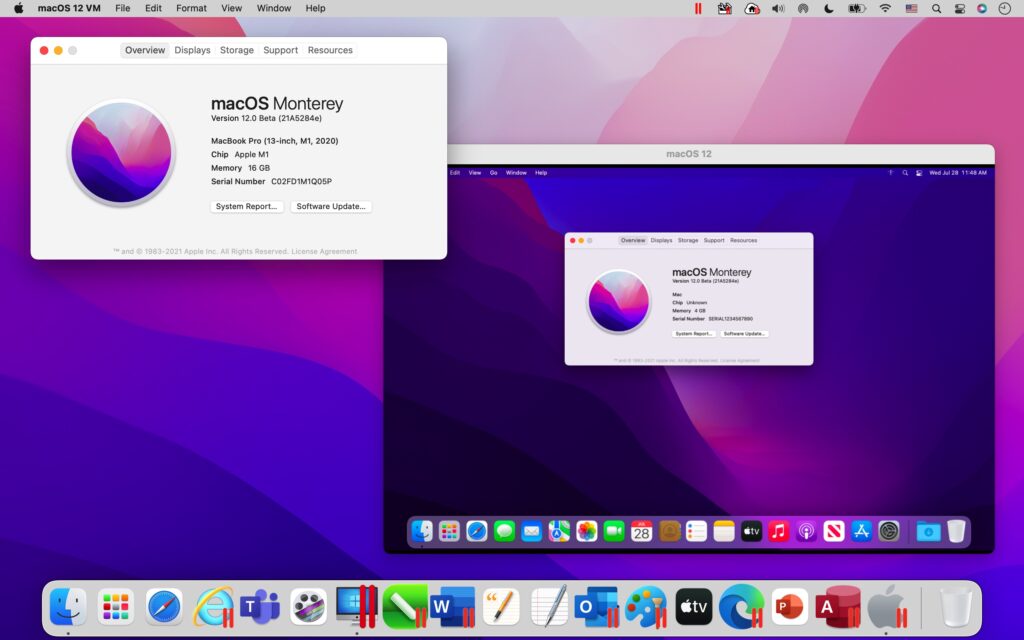
Virtualization makes it possible to create multiple virtual machines, each with their own operating system (OS) and applications, on a single physical machine. They are often referred to as a guest while the physical machine they run on is referred to as the host. What is a virtual machine (VM)?Ī virtual machine is a virtual representation, or emulation, of a physical computer. An introduction to Virtual Machines (VMs), technology for building virtualized computing environments and the foundation of the first generation of cloud computing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
